Secure Your Future: Unveiling The Power Of Retirement Savings Act 1997 – Act Now!
Retirement Savings Act 1997: A Comprehensive Guide to Secure Your Future
Introduction
Dear Readers,
1 Picture Gallery: Secure Your Future: Unveiling The Power Of Retirement Savings Act 1997 – Act Now!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the Retirement Savings Act 1997. In this article, we will delve into the details of this important legislation that aims to provide financial security for individuals during their golden years. Understanding the intricacies of this act is crucial for anyone planning for retirement. So, let’s explore what the Retirement Savings Act 1997 entails and how it can benefit you.
Overview of the Retirement Savings Act 1997

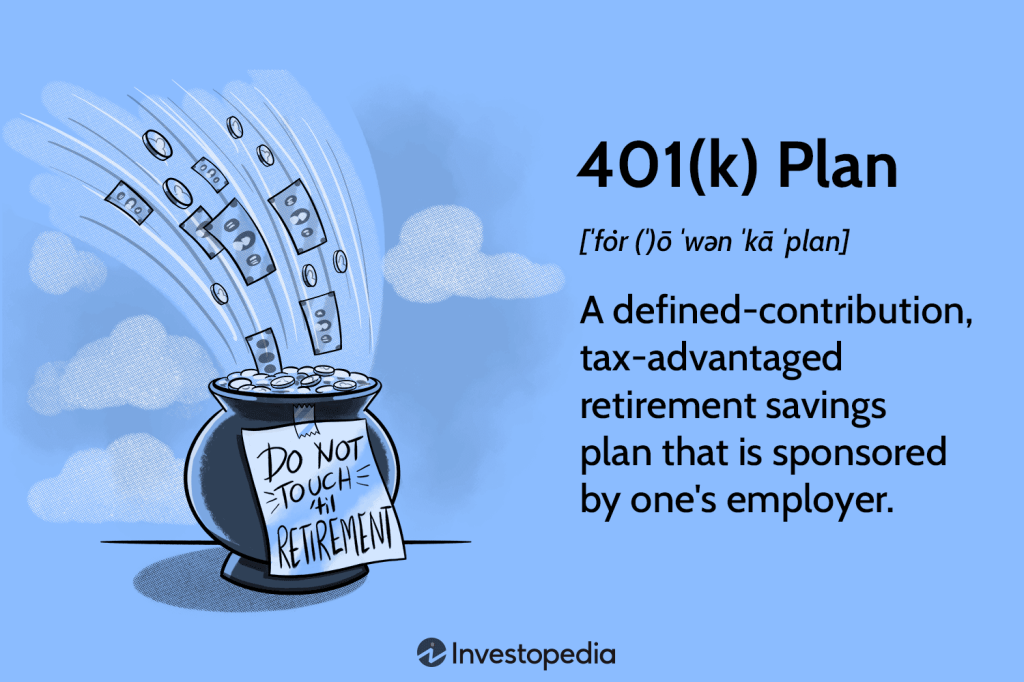
Image Source: investopedia.com
The Retirement Savings Act 1997 is a legislation that was enacted to encourage individuals to save for retirement and ensure their financial well-being during their post-employment years. It offers various tax incentives and benefits to individuals who participate in retirement savings plans.
What is the Retirement Savings Act 1997?
🔍 The Retirement Savings Act 1997 is a piece of legislation that provides a framework for retirement savings plans and outlines the rules and regulations governing these plans. It aims to incentivize individuals to save for retirement and secure their financial future.
Who is Eligible under the Retirement Savings Act 1997?
🔍 The act is applicable to all working individuals who are looking to save for retirement. It covers employees, self-employed individuals, and even those who are not currently employed but wish to contribute to a retirement savings plan.
When was the Retirement Savings Act 1997 Enacted?
🔍 The Retirement Savings Act 1997 was enacted on [insert date]. It has since been amended and updated to meet the evolving needs of retirees and address any potential gaps in the legislation.
Where Does the Retirement Savings Act 1997 Apply?
🔍 The Retirement Savings Act 1997 applies to [insert jurisdiction]. The act provides guidelines and regulations that are specific to this jurisdiction, ensuring uniformity and clarity in retirement savings planning.
Why Was the Retirement Savings Act 1997 Introduced?
🔍 The Retirement Savings Act 1997 was introduced to address the growing concern of inadequate retirement savings among individuals. It aims to promote long-term financial stability and reduce reliance on government-funded retirement programs.
How Does the Retirement Savings Act 1997 Work?
🔍 The act enables individuals to contribute a portion of their income to retirement savings plans, such as pension funds or individual retirement accounts (IRAs). These contributions are often tax-deductible, providing immediate financial benefits. The funds accumulated in these plans grow tax-free until retirement, ensuring a secure nest egg for the future.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Retirement Savings Act 1997
Advantages:
1. 🌟 Tax Incentives: The act provides tax deductions on contributions made to retirement savings plans, reducing the tax burden on individuals.
2. 🌟 Financial Security: By participating in retirement savings plans, individuals can secure their financial future and have a stable income during retirement.
3. 🌟 Employer Contributions: Many employers match their employees’ contributions, effectively doubling the savings and accelerating the growth of retirement funds.
4. 🌟 Investment Growth: The funds invested in retirement savings plans have the potential to grow over time, ensuring a higher return on investment.
5. 🌟 Flexibility: The act allows individuals to choose from various retirement savings plans that best suit their needs and risk appetite.
Disadvantages:
1. ⚠️ Contribution Limits: The act imposes limits on the amount individuals can contribute to retirement savings plans, which may restrict higher earners from fully maximizing their savings.
2. ⚠️ Early Withdrawal Penalties: Withdrawing funds from retirement savings plans before reaching retirement age may result in penalties and taxes, discouraging premature withdrawals.
3. ⚠️ Market Volatility: Retirement savings plans are subject to market fluctuations, which may impact the growth and value of the investments.
4. ⚠️ Lack of Accessibility: The funds in retirement savings plans are typically inaccessible until retirement age, which may limit immediate financial needs.
5. ⚠️ Regulatory Changes: The act may undergo amendments and modifications, which could impact the rules and benefits associated with retirement savings plans.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Retirement Savings Act 1997
1. Can I contribute to a retirement savings plan if I am self-employed?
Yes, self-employed individuals are eligible to contribute to retirement savings plans under the Retirement Savings Act 1997. They can choose from various options, such as a Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA or a solo 401(k) plan.
2. What happens if I exceed the contribution limits set by the act?
If you exceed the contribution limits, the excess amount may be subject to taxes and penalties. It is important to stay within the allowable limits to avoid any adverse consequences.
3. Are employer contributions mandatory under the act?
No, employer contributions are not mandatory under the act. However, many employers choose to match their employees’ contributions as an added benefit.
4. Can I withdraw funds from my retirement savings plan before retirement age?
While it is generally discouraged, you may be able to withdraw funds from your retirement savings plan before retirement age in certain circumstances, such as financial hardship or qualifying medical expenses. However, early withdrawals may be subject to penalties and taxes.
5. What happens to my retirement savings plan if I change jobs?
If you change jobs, you have several options for your retirement savings plan. You can leave the funds in your previous employer’s plan, roll them over into a new employer’s plan, transfer them to an individual retirement account (IRA), or cash out the funds (subject to taxes and penalties).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Retirement Savings Act 1997 plays a vital role in ensuring a secure financial future for individuals during their retirement years. By taking advantage of the tax incentives and benefits offered under this act, individuals can actively contribute towards building a substantial nest egg. However, it is important to carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages associated with retirement savings plans and make informed decisions based on personal circumstances.
Final Remarks
Dear Readers,
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into the Retirement Savings Act 1997. While we have strived to present accurate and up-to-date information, it is always advisable to consult with a financial advisor or legal professional for personalized advice. Planning for retirement is a crucial step towards securing your financial well-being, and the Retirement Savings Act 1997 can serve as a valuable tool in achieving that goal.
This post topic: Budgeting Strategies